Cell Cycle
Hey guys, Welcome back to the bioeducation1. In this post you will learn about the Meiosis. In the previous post we talked about the mitosis, now Meiosis. Let's go to the topic:- Cell Cycle- Meiosis.
Cell Cycle - Meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a complex type of cell division in which cell divides to form four daughter cells which involves the halving of chromosome number.
Characteristics of Meiosis:
- It occurs in diploid cell.
- It involves the halving of chromosome number. Therefore it is termed as Reduction Division.
- The Meiotic Division is to achieve rejuvenation and recombination.
- In this process, the chromosomes duplicate only once but cell divides twice. There is formation of four haploid cells.
- It is mainly associated with the formation of spores ( in Plants and Fungi) and formation of Gametes ( in Animals and Humans).
The Meiotic Division involves two successive divisions, Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The both division of which have Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis phases.
Interphase:
- It is similar to that in mitosis.
- It was formerly called resting phase since the cell is highly active and prepare itself for the cell division hence is called the preparatory phase.
- This phase occupies 95% portion of cell cycle.
- The Interphase can be further divided into G1 phase, S phase and G2 phase.
- G1 phase- It is the first growth phase also called the post-mitotic gap phase. As the name suggest the cell growth take place in this phase. It involves synthesis of proteins and molecules required for DNA replication. Depending on the cell this phase can be last for days, months or years. The cell may withdraw from cell cycle and can enter into the G0 or quiescent stage. The cell which has gone in G0 state may reenter the G1 phase or may get differentiated to become permanent cell.
- S-phase- It is also called phase of Synthesis. Replication of DNA takes place during this stage. Genetic Material i.e. DNA duplicates. Nucleus becomes double in size. Chromosome replication takes place. Histone proteins are also produced. Once DNA replication is completed, the cell contains twice the total number of chromosomes and hence it is prepared for G2 phase.
- G2 phase- It is second growth phase also called the pre-mitotic gap phase. It involves the Synthesis of tubulin, spindle protein and RNA. There is duplication of cell organelles such as centriole, chloroplasts and mitochondria. It is also phase which check the duplication of all cell organelles and proteins has taken place or not. This is the last chance for the organelles to duplicate. If everything is perfect the cell is ready to go for meiotic phase.
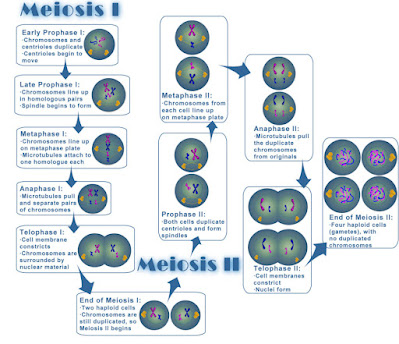
Karyokinesis:- It is nuclear division in which nucleus undergoes a series of changes to form the daughter nuclei.
Karyokinesis includes the four phases like Mitosis i.e. Prophase-I, Metaphase-I, Anaphase-I and Telophase-I.
1. Prophase-I
- It is the most complicated and longest phase of Meiosis.
- It is further distinguished into the Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
Leptotene
- It is also called Leptonema
- During the phase, the chromatin network condenses amd resolves into long and thin, thread-like chromosomes.
- Now, each chromosome consist of two chromatids.
Zygotene
- This phase is also called Zygonema
- During this phase, the homologous chromosomes begin to pair. Such a pairing is called Synapsis.
- Each pair of chromosomes is facilitated by the synaptonemal complex.
- The pairing at this stage is called bivalents.
Pachytene
- Pachytene is also called the Pachynema which means thick thread.
- The condensation of chromosomes progresses and they become thick and short.
- There is Formation of tetrad (composed of four chromatid)
- During this process, the crossing over i.e. exchange of genetic material takes place between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
- The site where crossing over take place is called chiasmata.
Diplotene
- This phase is also called Diplonema.
- The homologous chromosomes now start repelling to each other and begins to separate.
- However, they remain attached at the point where crossing over takes place, thus chiasmata can be seen.
- Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane can be seen.
Diakinesis
- Chromosomes continue to condense and shorten.
- The chiasmata get shifted to the end of chromatids due to the separation of Homologous chromosomes. This process is called Terminalisation.
- The Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane completely disappear and there is formation of spindle fibres.
2. Metaphase-I
- The spindle formation is completed and the chromosomes move and arrange themselves at the Equatorial plane.
- The mitotic spindle fibre is attached to each of the sister chromatids.
- Microtubules attached to one homologue each Disjunction
- Chromosomal fibres extend from the pole to the centromeres of corresponding homologues (Homologous chromosomes).
3. Anaphase-I
- The chromosomal fibres contract and pull the homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes start moving towards the opposite poles.
- The homologous chromosomes which was still attached during the Diakinesis, finally get separated and this process is called Disjunction.
- Now Each chromosome is having one centromere and two chromatids (exchanged segments).
- At the end, half the number of chromosomes gather at respective poles.
4. Telophase-I
- The chromosomes get uncoiled to form chromatin.
- The spindle fibre disappear, Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane start reappearing
- There is formation of two daughter nuclei.
- The Telophase-I is often follow by division of cytoplasm.
Cytokinesis:-
- The cytoplasm divides in this process, In animal cells the plasma membrane constricts in the middle while a cell plate is formed in plant cell to form daughter cell.
- There is formation of haploid cell (consist of single set of chromosomes).
Interkinesis
A very short period between Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II. It may or may not be present in the cell.
Meiosis-II
Meiosis-II also consists of two sub-stages i.e. Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis.
Both the haploid daughter cells formed at the end of Meiosis-I undergo Meiosis-II simultaneously that maybe with or without interkinesis. The Meiosis-II process is almost similar to Mitosis.
Karyokinesis-II
Prophase-II
- During this phase, the chromosomes with chromatids become distinct.
- The condensation of chromosomes take place.
- The Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane disappear.
Metaphase-II
- During this phase, the spindle formation take place and the chromosomes move towards the Equatorial plane.
- The chromosomes get connected to the respective poles by the chromosomal fibres.
Anaphase-II
- The centromere of each chromosome divides and chromatids get separated. Each chromatid is called daughter chromosome.
- They move towards the opposite pole by the contraction of chromosomal fibres and elongation of Inter-chromosomal fibres.
Telophase-II
- The daughter chromosomes which was arranged at each pole starts uncoiling.
- The Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane start reappearing around each group of chromosomes forming two daughter nuclei.
Cytokinesis-II
Telophase-II is followed by division of the cytoplasm of cell forming two daughter cells. At the end of Meiosis-II
four daughter cells are formed. The cells were haploid.
Significance of Meiosis:
- It produces haploid gametes for Sexual Reproduction.
- It helps to maintain the chromosome number constant in a given species.
- It introduces genetic recombinations leading to variations and evolution.
- Meiosis produces genetic variation by the process of recombination.
If you want to read about the mitosis.
If you like our content don't be hesitate to share it with your friends and family members.
If you like to read the Educational Blog, you can read in:- bioeducation1.blogspot.com

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any query, please let me know.